
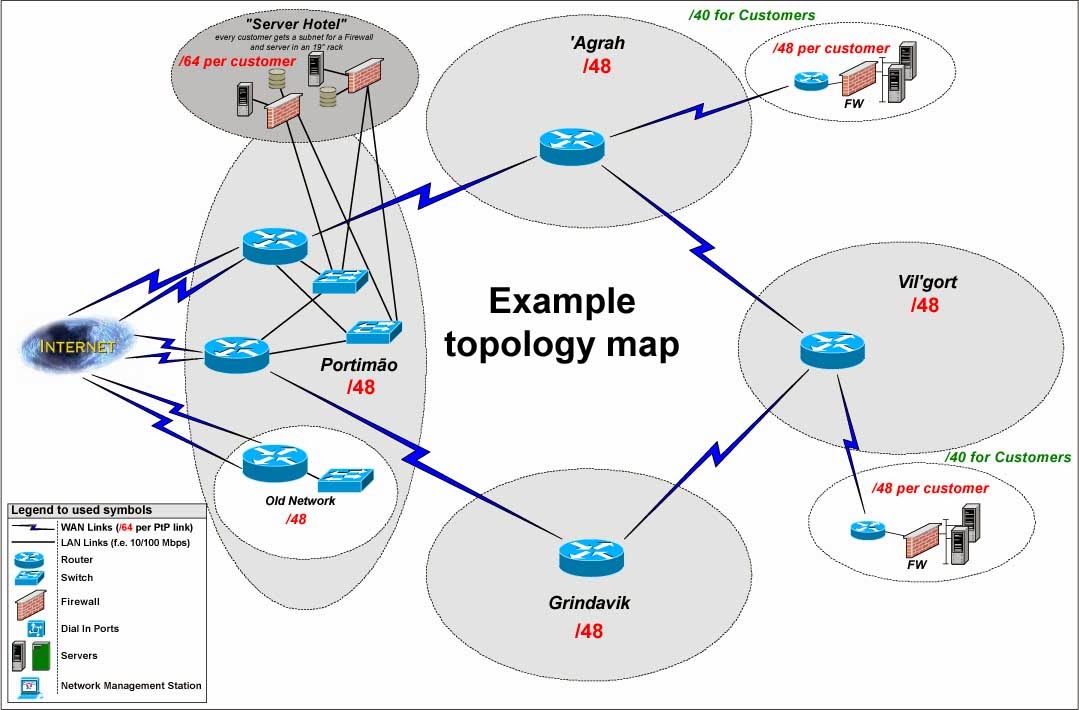
Let’s assume Controller advertises BGP LU routes for E2, i.e., 11.0.0.2/32, with next-hop set to loop-back IP address of ASBR1, that is, 1.1.1.1 and a label 111 to R1 & R2. BGP LU can be used here to perform traffic engineering or selecting Egress peer through which traffic should be forwarded.Ī Centralized EPE Controller can be used to establish iBGP session with R1 and R2. Traditional Destination based routing enforced by BGP policy and best path selection on the ASBRs may route traffic to a single AS as exit when a case can be made that for some prefixes an exit via some other AS may be preferable. Any traffic destined to prefix 50.0.0.0/8 from R1 will always be tunneled to ASBR1 and then it will always be sent on an interface connected to E1. ASBR1 advertises this prefix to both R1 & R2. Prefix 50.0.0.0/8 next-hop 11.0.0.2 as-path 3 200 300 from E2.īGP path from E1 will be selected as best path due to shorter AS path length. Consider following BGP updates are received on ASBR1: eBGP session is present between ASBR1 & E1, ASBR1 & E2, ASBR2 & E3 and ASBR2 & E4.
Network topology mapper bgp peering device full#
There exists an iBGP Full Mesh between R1, R2, ASBR1 & ASBR2. Let’s assume reachability of loop-back addresses 1.1.1.1, 2.2.2.2, 3.3.3.3 & 4.4.4.4 through LDP or Segment Routing (SR). R1, R2, ASBR1 & ASBR2 could be connected each other directly or reachable to each other over an IGP (OSPF/ISIS) or MPLS tunnel. As shown in Figure 1 below R1, R2, ASBR1 & ASBR2 are in AS 1 and E1, E2, E3 & E4 are in different Ases. The following two use cases explain how BGP LU path next-hop resolution over tunnels would help in achieving desired or efficient traffic forwarding.Įgress Peer Engineering is a source-routing paradigm that provides ability to select an egress node/interface through which traffic goes out of an Autonomous System (AS).
Network topology mapper bgp peering device update#
UPDATE messages also list destinations to which the router no longer offers connectivity.īGP detects and eliminates routing loops while making routing policy decisions by using the network topology as defined by AS paths and path attributes. The route description includes the destination prefix, prefix length, autonomous systems in the path, the next hop, and information that affects the acceptance policy of the receiving router. If an UPDATE message contains an error, the router sends a NOTIFICATION message and transitions to the Idle state.ĭuring established BGP sessions, routers exchange UPDATE messages about the destinations to which they offer connectivity.
If the timeout expires or an error condition exists, the router transitions to the Idle state. If the message is received prior to a timeout expiry, the router transitions to the Established state.

BGP defines a state machine for establishing connections.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
